Note Dr. Andrés Medrano, medical specialist in urology, about Kegel Exercises and their importance in the treatment of Urinary Incontinence.
Urinary incontinence is a condition that affects many women, characterized by the involuntary loss of urine, which can be uncomfortable and embarrassing. There are two main types: stress incontinence, which is caused by the weakness of the tissues of the pelvic floor, and urge incontinence, also known as an overactive bladder, which involves involuntary contractions and an urgent feeling of needing to urinate. Factors such as obesity, the number of births and genetics may predispose women to the incontinence of effort, while age and the changes postmenopáusicos are common in urge incontinence.
Kegel Exercises: A Non-Invasive Solution
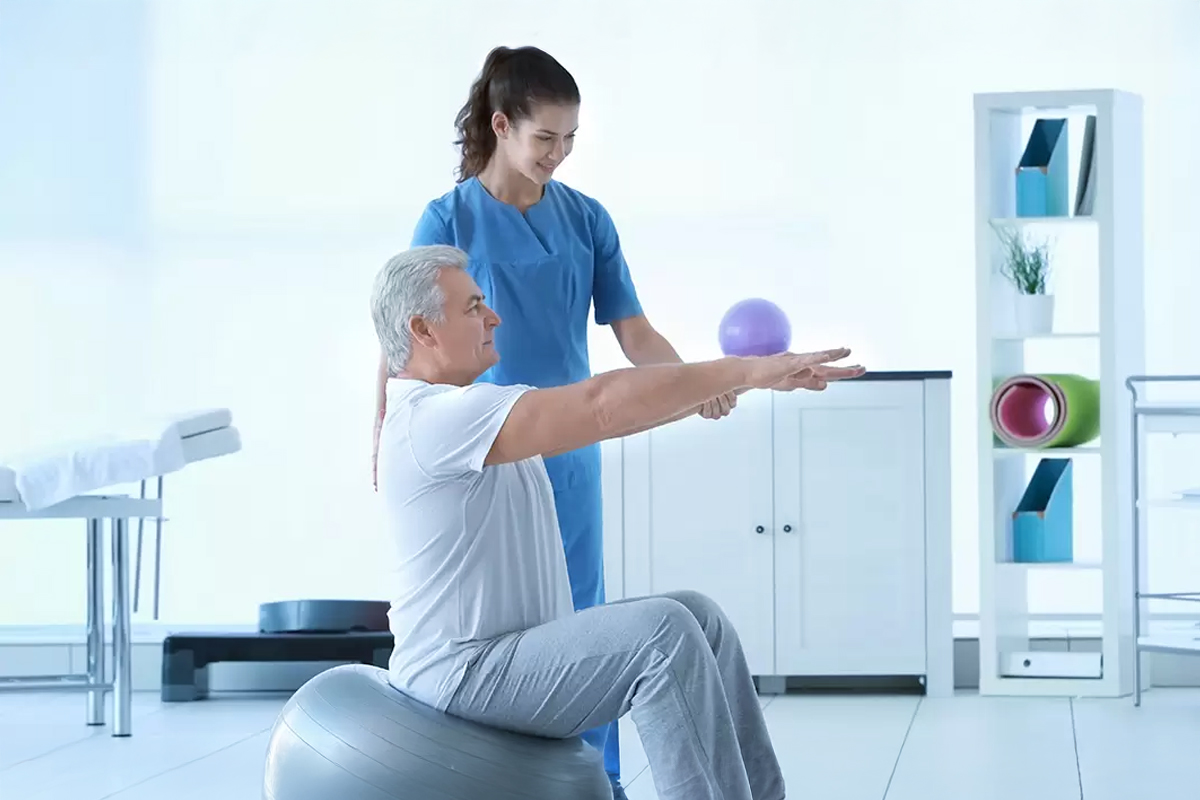
Kegel exercises are presented as a non-invasive solution to treat urinary incontinence. These exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles that surround the urethra and are especially useful for those who suffer from stress urinary incontinence. It is recommended that these techniques are taught by a specialist in kinesiology with experience in rehabilitation of the pelvic floor, to ensure that they perform properly and effectively.
How to Perform Kegel Exercises
The practice consists of alternating contraction and relaxation of the anal sphincter, which also affects the urethral sphincter. To get results, it is advised to perform four sets of ten contractions daily, gradually increasing the duration of the contractions from one second to five. Kegel exercises are safe and can be performed during pregnancy and the postpartum period, many women experience incontinence in these stages.
Treatment options Advanced
If the exercises do not achieve satisfactory results, it can be considered the surgical treatment, especially for stress urinary incontinence. In addition, there are other options such as the rehabilitation of the pelvic floor biofeedback, stimulation of the posterior tibial nerve, and pharmacological treatments for urge incontinence. Ultimately, if these approaches don't work, you can explore the more advanced therapies like the injection of botox into the bladder or sacral neuromodulation.
Read full article: