The human papilloma virus (HPV) causes warts. There are more than 40 strains of HPV that affect the genital area. Genital warts are one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections. Usually affect the moist tissues of the genital area. It is manifested as small bumps . In most cases, the warts are too small to be visible. Some strains of genital HPV can cause genital warts, while others can cause cancer. Vaccines can help prevent certain strains of genital HPV.
Diagnosis
Genital warts are mostly diagnosed by their appearance. However, sometimes it may be necessary to perform a biopsy and send it to analyze.
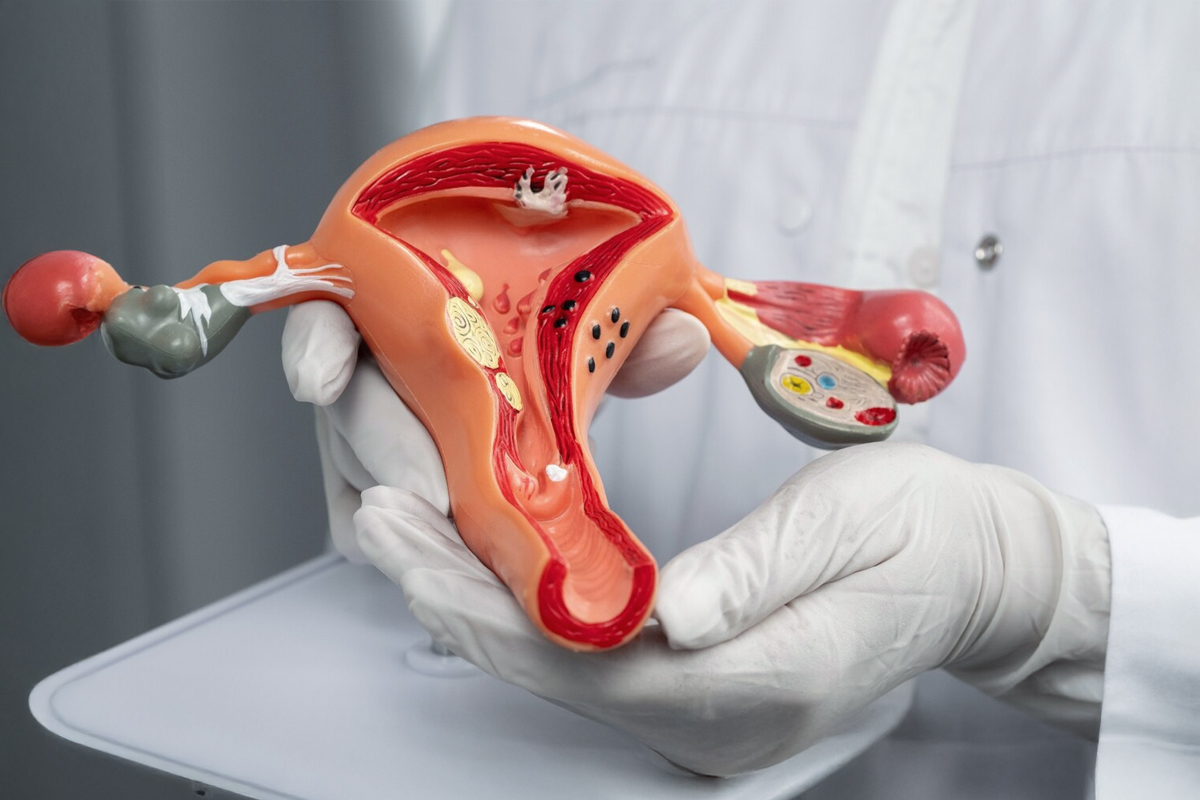
Women should perform regular pelvic exams and pap smear (Pap test), which may help to detect the changes of vaginal and cervical caused by genital warts or early signs of cervical cancer.

Symptoms
In women, genital warts can occur on the vulva, the walls of the vagina, the area between the external genitals and the anus, and the cervix. In men, they usually appear on the tip or shaft of the penis, the scrotum, and/or the anus.
The signs and symptoms of genital warts may include:
- Swelling, small, brown or pink in the genital area.
- A form similar to that of a cauliflower caused by several warts very close to one another.
- Itching or discomfort in the genital area.
- Bleeding in sex
Vaccination
In Argentina, we recommend routine vaccination against human papillomavirus for girls and boys from the age of 11. You receive two doses of the vaccine against the human papilloma virus with at least six months apart. It is ideal that you get the vaccine before they have sexual contact. The side effects of the vaccine are usually mild and include pain at the injection site, headaches, low-grade fever or symptoms similar to the flu.
Leave a link with information about the steps to follow in Argentina: https://www.argentina.gob.ar/salud/vacunas/vph
Treatment for genital warts
If the warts do not generate discomfort in the patient, it is possible that you may not need treatment. If, on the contrary, symptoms such as itching, burning and/or pain, or concern for the spread of the infection is intranquilizadora, you can remove an outbreak with drugs, treatments or surgery.
Medications for genital warts
The treatments more common for genital warts that can be applied directly on the skin include the following:
- Imiquimod: cream. Avoid sexual contact while the cream is on your skin. A possible side effect is redness of the skin. Other side effects may include blistering, pain or discomfort in the body, cough, rash, and fatigue.
- Trichloroacetic acid: This treatment chemical burns genital warts and can be used for warts internal. Side effects may include mild skin irritation, sores or pain.
Surgery
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen (cryotherapy).
- Electrocautery.
- Surgical excision.
- Laser treatments.