Lithiasis (stone, stone)
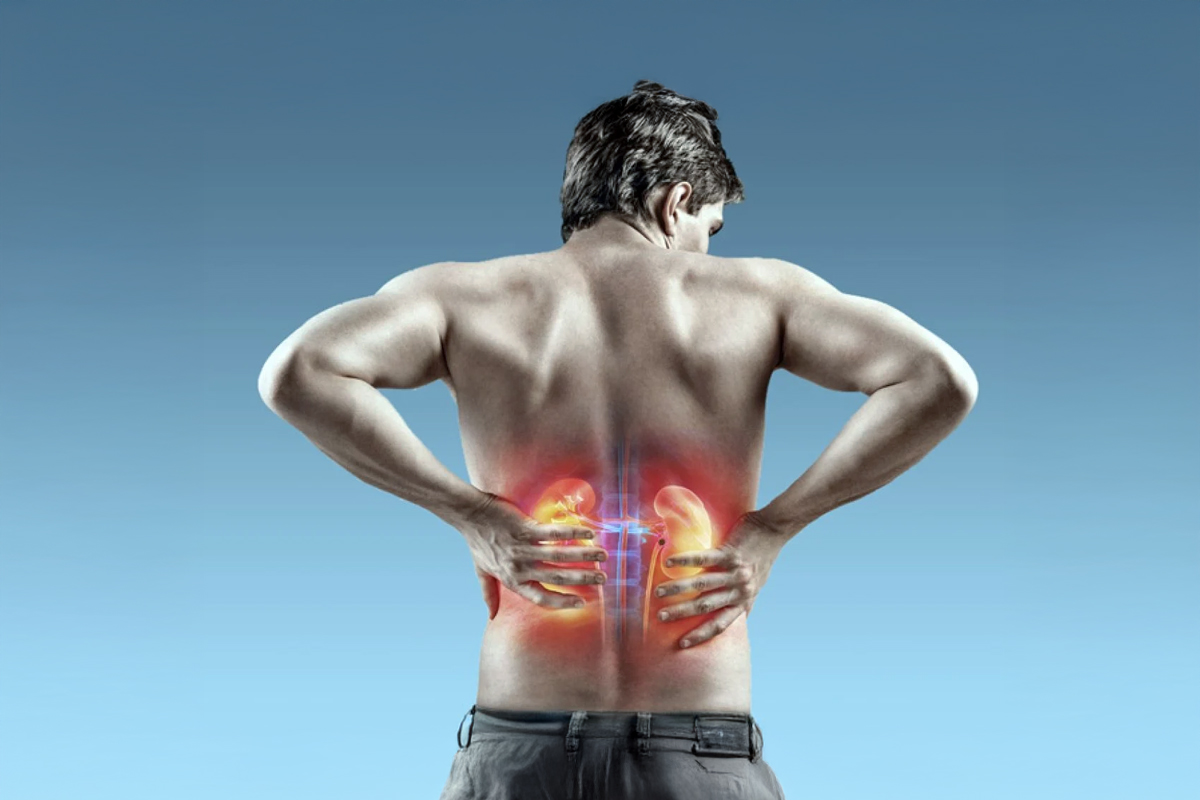
Cuando nos referimos a litiasis urinaria, estamos hablando de una enfermedad causada por la presencia de cálculos (piedras) que se encuentran en el interior de los riñones o de las vías urinarias (uréteres o vejiga). En general, la litiasis urinaria se forma en nuestro interior cuando la orina se concentra, lo que permite que los minerales se cristalicen y se unan.

Causes
La actual información con la que los Médicos Urólogos cuentan actualmente, sobre el conocimiento de los mecanismos fisiopatológicos responsables de la formación de las litiasis, junto al historial médico de cada paciente, les permite elegir el mejor tratamiento para la resolución de las litiasis urinarias, así como también para la prevención futura de las mismas.
Factors that favors the formation of stones:
- Intake of some liquid, which generates little desire to urinate (pee).
- A family history of kidney stones.
- History of previous personal (if you already had one or more kidney stones, there is a greater risk of having to re-train them, if you do not make a right treatment).
- Eating a diet rich in protein, sodium (salt) and sugar.
Symptoms
May go unnoticed or cause:
- Renal colic: Dolor muy intenso en la zona baja de la espalda que se puede irradiar hacia el abdomen o hacia los genitales.
That may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, sweating. - Hematuria: it Is the appearance of blood in the urine. You can be visible to the naked eye or not. It is produced by the lesions produced by the calculation in its passage through the urinary tract.
- Infections of the urinary tract: kidney stones may be the cause or the consequence of frequent urinary tract infections.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of urinary stones is recommended to increase the intake of fluids (preferably water), bring a low-salt diet, limiting the intake of meat, sugar and alcohol.
It is of importance to study the characteristics of the urine and perform a blood test to modify possible alterations that are generating the formation of urinary stones.
Diagnosis
- Analysis of the urine: to search for the presence of blood or pus, or small crystals that form the calculation.
- Analysis of the calculations expelled or recovered in the surgery: in order to know the composition of the same, and to determine its origin. This will allow you to make the appropriate treatment to prevent the formation of most urinary stones.
- Imágenes: Se suelen solicitar radiografía de abdomen, ecografía abdominal y tomografía, entre otros estudios.
Treatment
- Medication: Usuallydepending on the size, and other considerations of urolithiasis, is commonly prescribed medication as a first step, in order that the patient can expel urolithiasis.
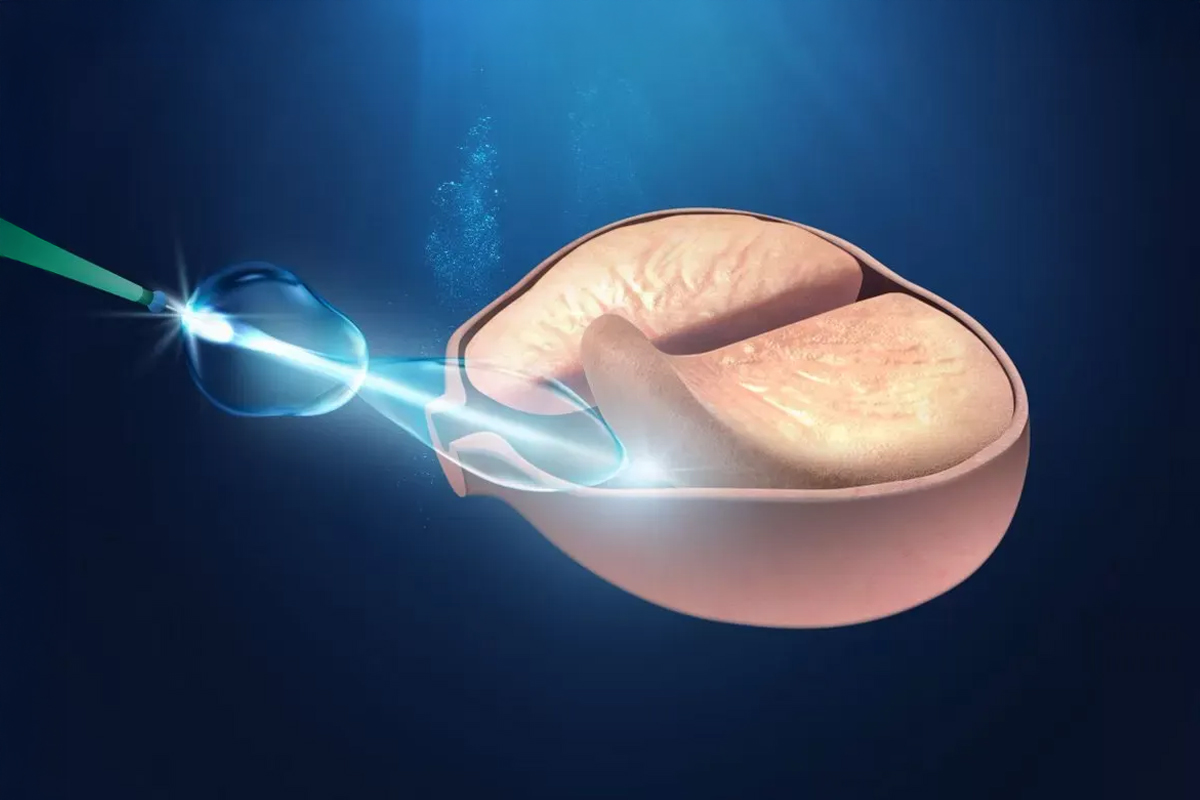
- Extracorporeal shock wave: it is an outpatient treatment for 45 min approx. that consists of fragmenting the calculations and that these, then, are eliminated in the form of grit through the urine.
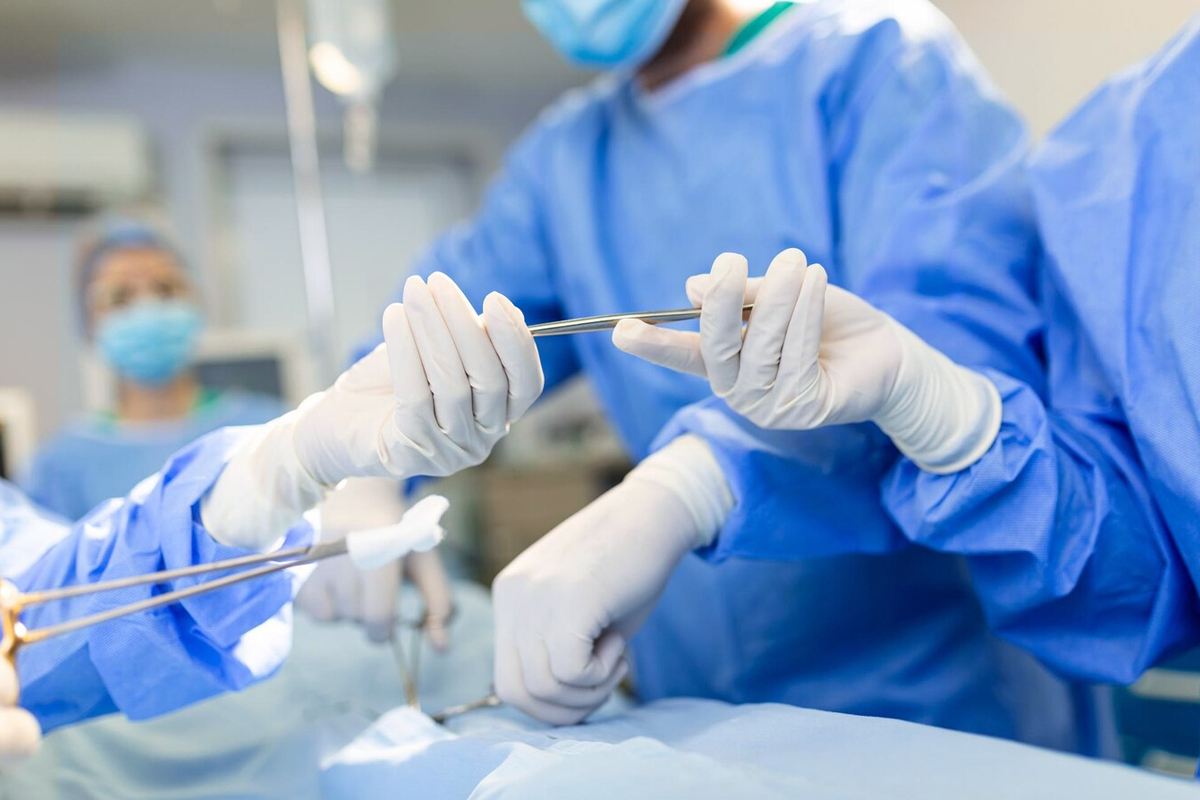
- Procedures endourológicos: Cirugia mínimamente invasiva para la extracción de los cálculos urinarios.