Prostatitis and infection of the prostate:
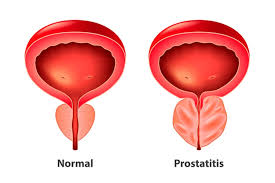
Prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate gland that can affect men of any age. Is presented in different types, being the prostatitis acute bacterial, chronic bacterial prostatitis and prostatitis, chronic nonbacterial the most common. The bacterial prostatitis occurs when there is a bacterial infection in the prostate, while the prostatitis, chronic nonbacterial is not associated with bacteria.
Some patients need psychological support to travel this pathology, as in some men, the urinary symptoms are painful and prolonged duration.
Symptoms:
Usually, the infections of the prostate. son casi asintomáticas o cursan con síntomas leves que son diagnosticados como infección urinaria o incluso un cuadro gripal. Pero no todos los pacientes presentan los mismos síntomas en los episodios de prostatitis y algunos pueden llegar a ser muy sintomáticos y su calidad de vida puede estar comprometida por esta patología.
Some of the most common symptoms are:
- Chills.
- General malaise, muscle aches, lumbago.
- Fever.
- Redness of the skin.
- Blood in the urine.
- Burning or pain during urination.
- Difficulty starting urination.
- Difficulty emptying the bladder.
- Urgent need to urinate.
- Incontinence of urine.
- Urine foul-smelling.
- A urine stream is weak.
- Pain or discomfort in the abdomen above the pubic bone, in the lumbar region, in the area between the genitals and the anus, or in the testicles.
- Pain with ejaculation or blood in the semen.
- Pain with bowel movements.
Symptoms:
The grounds for germs to reach the prostate gland and cause prostatitis, are very varied. Inflammation of the prostate gland (prostatitis) can occur for a variety of sources, for example, any bacteria that can cause a urinary tract infection, could lead to prostatitis, including some sexually transmitted diseases can also cause bacterial prostatitis; prostatitis can also be caused by problems in the urethra, for example: Obstruction of the bladder outlet, or by inability to retract the foreskin (phimosis), by an injury in the area between the scrotum and the anus (the perineum) or also after having a catheter in the bladder, any endoscopy or biopsy of prostate.
Men who suffer enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) have a higher risk of developing prostatitis. As the prostate gland may become blocked, which will facilitate the growth of the bacteria. It is interesting to note that the symptoms of chronic prostatitis can be very similar to the enlargement of the prostate gland (BPH), and is the Urologist who, with his medical examination and the results of the relevant studies, you need to assess your condition.
We leave a small list of the most common causes that may lead to patients undergoing one prostatitis:
- Patients who were performed a prostate biopsy.
- Patients studies were performed medical minimally-invasive procedures.
- Diseases of the prostate: BPH, prostate Cancer.
- Sexually transmitted diseases.
- Problems in the urethra.
- With a lot of often occur without apparent cause.
Diagnosis:
The Urologist who evaluates you will be asked some or all of the following medical tests to verify the diagnosis of prostatitis and to know what is the type of prostatitis should be treated:
Analysis of urine, prostate massage for obtaining the secretion of the prostate for cultivation, transrectal ultrasound of the prostate, blood, (it Is important to know that prostatitis can affect the results of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA), giving a value much above normal, on this blood test used to detect prostate cancer), among other studies that the doctor deems necessary, according to the medical history of the patient.
Evaluating your symptoms and the results of the clinical analysis, the urologist can conclude what kind of prostatitis treated the patient.
Classification of Prostatitis:
There are several types of prostatitis:
- Bacterial Prostatitis-acute: this type of prostatitis is typically begin suddenly, usually accompanied by symptoms similar to the flu, such as fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. Usually, it is caused by common bacteria.
- Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis: this type of prostatitis lasts usually 3 months or more. It originates when the antibiotics that are prescribed do not eliminate the bacteria that cause prostatitis. This generates that the patient may have recurrent infections and/or difficult to treat. We can say that when urinary symptoms and painful are recurrent, we have to think in a chronic prostatitis.
- Chronic Prostatitis or pelvic pain syndrome chronic. This type of prostatitis is not caused by bacteria, such as if you are the above. Usually, it often does not identify the exact cause that causes it. The symptoms vary in every man, in some, the symptoms are going through moments of more symptoms and then go on to a period of lower or no symptoms. This type of prostatitis, it is also called syndrome of chronic pelvic pain, which is divided in: pain Syndrome, chronic pelvic inflammatory Syndrome or pelvic pain chronic non-inflammatory.
Syndrome of pelvic pain (chronic Prostatitis)
Usually, the treatment of the syndrome of pelvic pain is very difficult and disappointing. Since the symptoms are persistent on the patient, and generates great discomfort in the quality of life, due to the pain, discomfort, voiding, and the (usual) failure of various medical treatments causes to the patient and their environment continuously in search of an answer.
There exist alternative physical therapies used to treat the symptoms of the syndrome of pelvic pain. Some of them are: the application of shock waves of low intensity, acupuncture, neuromodulation, laser prostate, injection of botulinum toxin, among others.
The application of shock waves in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain
Currently, the application of shock Waves in low-energy is used for various medical treatments, for example, in trauma, treat chronic pain, such as plantar fasciitis, tendonitis, etc, with very good results.
In the treatment of chronic pelvic pain, the application of shock waves of low energy is directed at the level of perineal and usually produces a significant decrease in pelvic pain, also showing an improvement in the discomfort of urination, which generates a good quality of life for the patient.
Treatment:
The Urologist to evaluate the treatment most appropriate to treat prostatitisdepending on how it manifests the symptoms in the patient and the type of prostatitis you have to try.
Usually in the treatment of prostatitis, chronic use of medication as a be alfabloquenates, relaxing bladder and/or anti-inflammatory drugs, it is often the most convenient, since the symptoms most predominant is the discomfort urinary irritativo.
Summary:
- Antibiotics: es el tratamiento que se utiliza con frecuencia para la prostatitis. El Urólogo deberá evaluar cual es el antibiótico mas adecuado, según el tipo de bacteria que esta provocando la prostatitis. Si los síntomas son graves, puede ser necesario que el antibióticos se suministre por vía intravenosa en un principio y luego se continúe por vía oral. Los pacientes con prostatitis crónica o recurrente, suelen tomar antibióticos por periodos prolongados. . Ya que habitualmente, los tratamientos antibióticos de periodos cortos fracasan y el paciente recaen con frecuencia en la prostatitis.
- Alpha-blockers: this type of medication is used to relax the muscle fibers and the neck of the bladder, which is where your prostate joins your bladder. This type of treatment, it may help to lessen the painful symptoms of the patient.
- Anti-inflammatory agents. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, can also help the patient to walk without pain, the symptoms of prostatitis.
- Changes in lifestyle: Los siguientes son algunos consejos que pueden ayudar al paciente a aliviar la sintomatología, por ejemplo: tomar un baño tibio (baño de asiento) o usa una compresa caliente, limitar o evita el alcohol, la cafeína y las comidas picantes y/o ácidas, evitar las actividades que pueden irritar la próstata, como pasar mucho tiempo sentado o andar en bicicleta. Es importante tomar bebidas sin cafeína, ya que esto hará que el deseo de orinar sea mayor y ayudará a eliminar las bacterias de la vejiga.