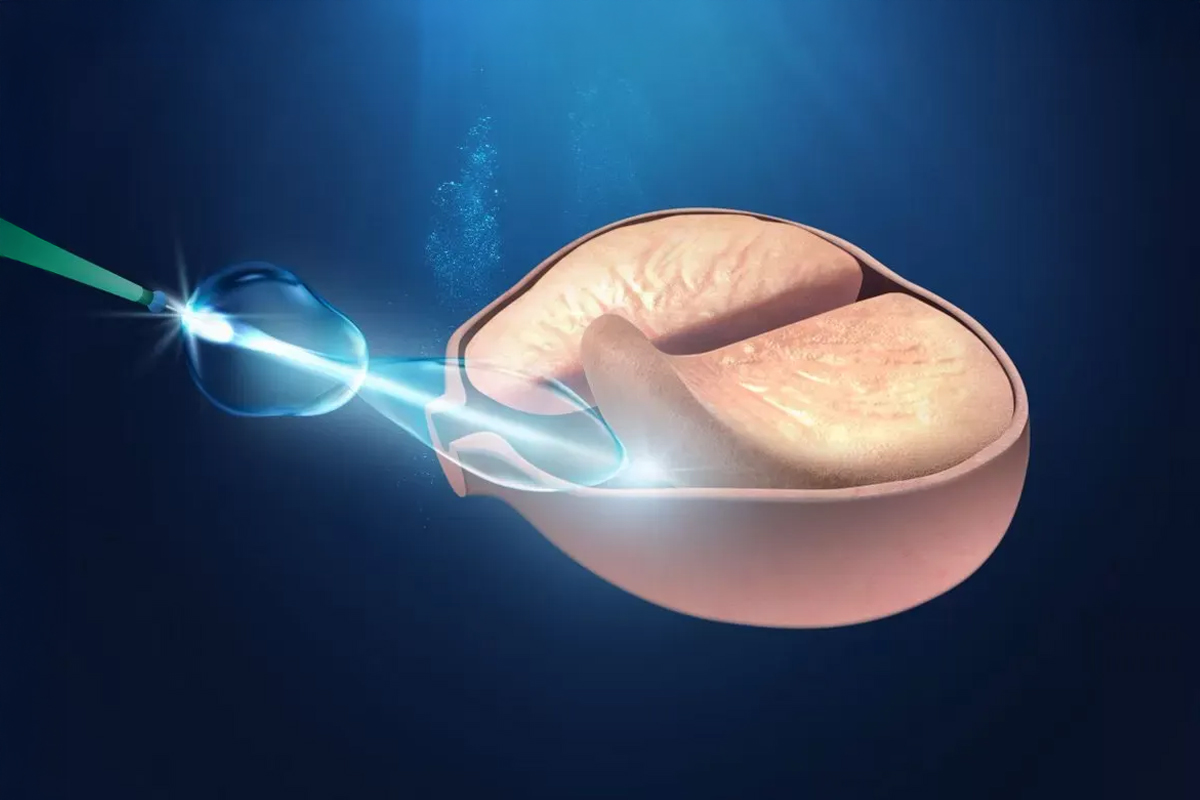
Why is it dangerous to hold back the urge to pee? Retain the urine in the normal way can have negative consequences for the health of the urinary system. When the kidneys produce urine, this descends into the bladder, which acts as a reservoir. As the bladder is full, it sends signals to the brain to indicate that it is time to empty it. However, when it postpones the act of urinating, the organism adapts to retain larger amounts of urine, which can alter the normal function of the bladder.
Enduring the urge to pee occasionally, for example, when you do not have access to a bathroom, it is usually not problematic. However, doing so frequently can generate what is known as “habit urinary retentive”. This habit can have several consequences, such as the over-stimulation of the pelvic floor muscles, which can hinder the start of urination. In addition, over time, the bladder can become used to store large volumes of urine, which reduces the sensitivity of the receptors in charge of notify that it is time to urinate.
A bladder altered in its form and function can become overactive or, in the long term, underactive. This means that you may be unable to contract properly, causing urination incomplete. Do not empty the bladder completely increases the risk of developing urinary tract infections and incontinence. May also cause a misalignment between the contraction of the muscle of the bladder and relaxation of the sphincter, resulting in an eject dysfunctional of the urine.
It is recommended to urinate between 6 and 8 times a day to maintain a healthy bladder. It is important not to rush the process and to empty the bladder completely each time the need arises. If doubts arise about the habits voiding, it is advisable to consult a health professional.
Note the Drs. Florence Colella and María Belén Maza, medical urólogas.
Whole note: